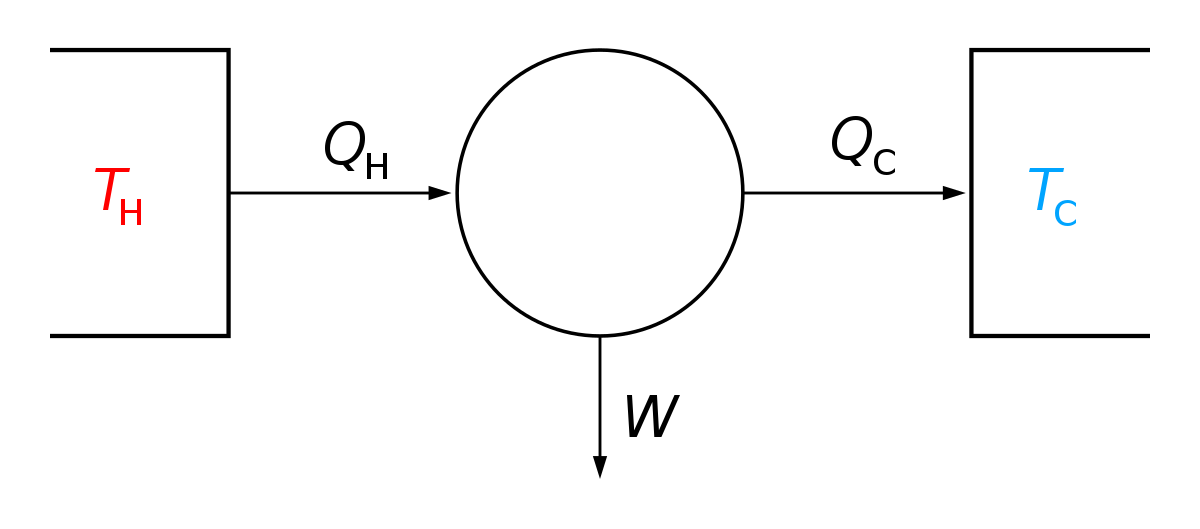
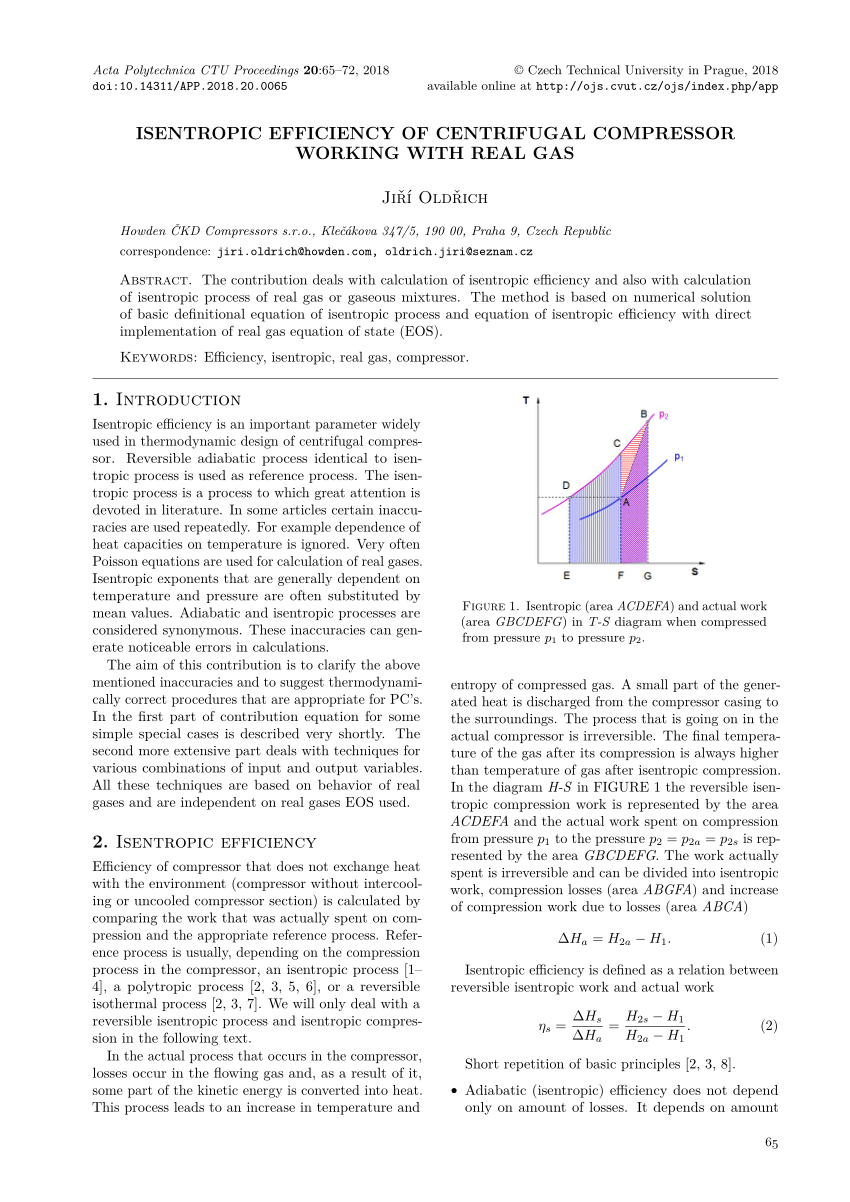
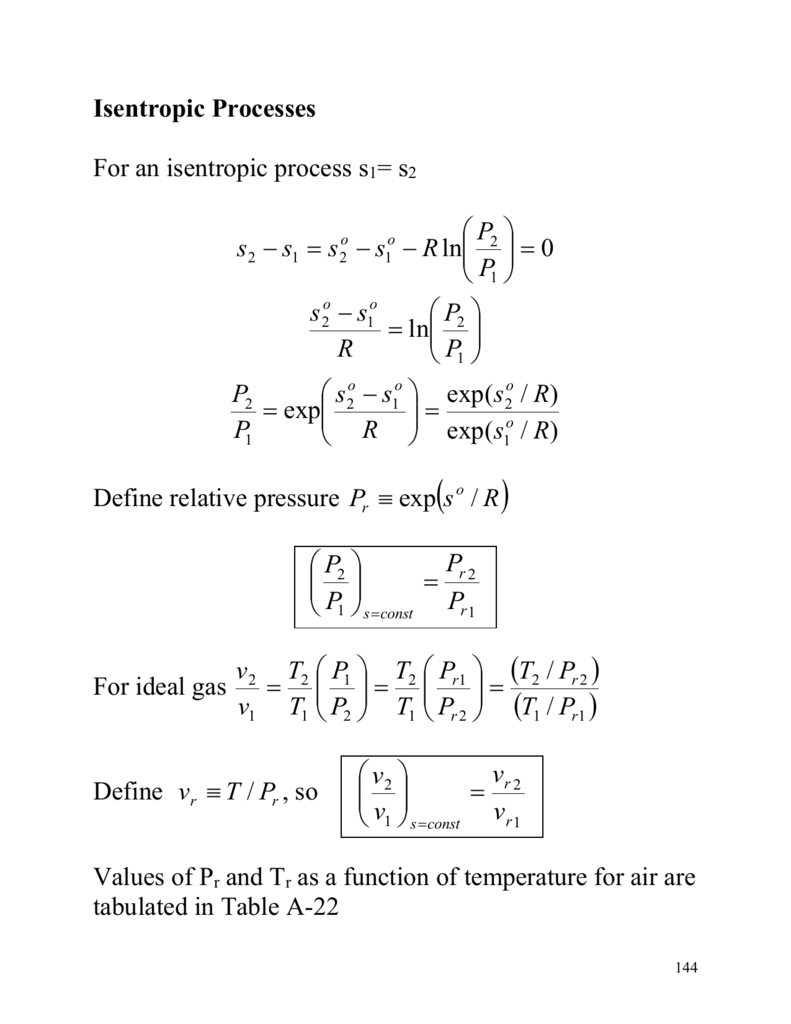
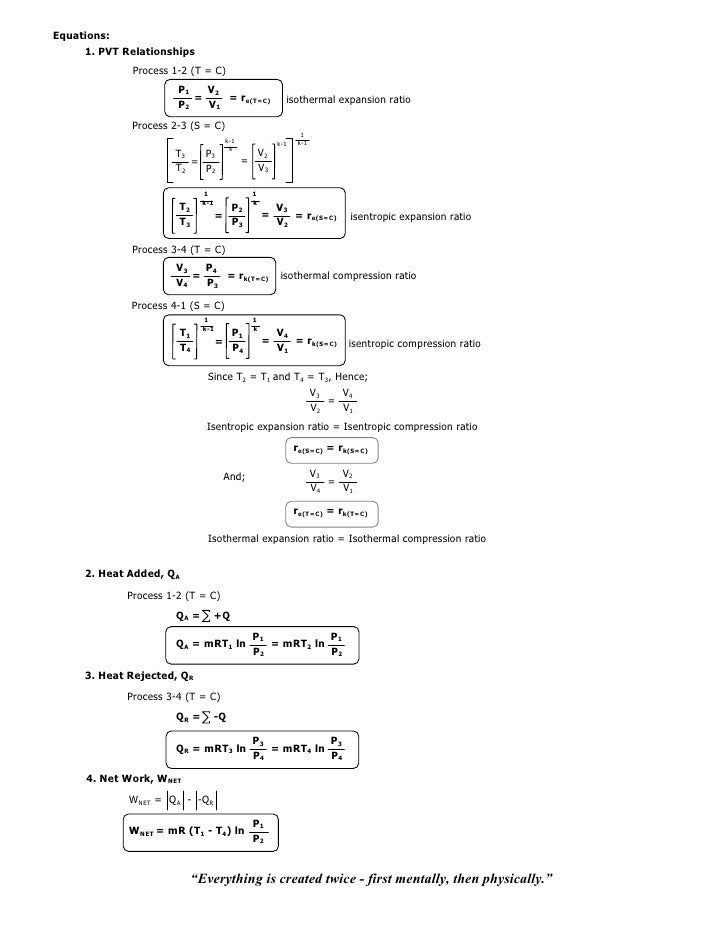
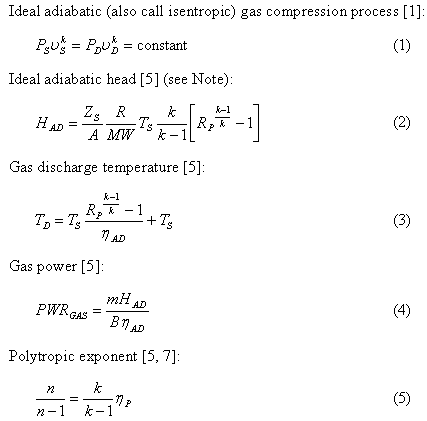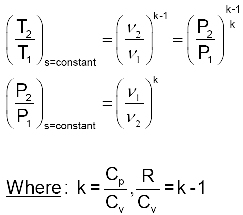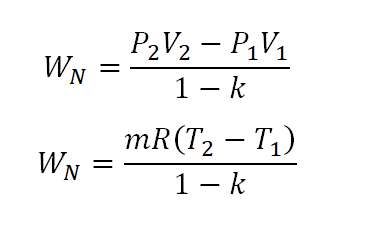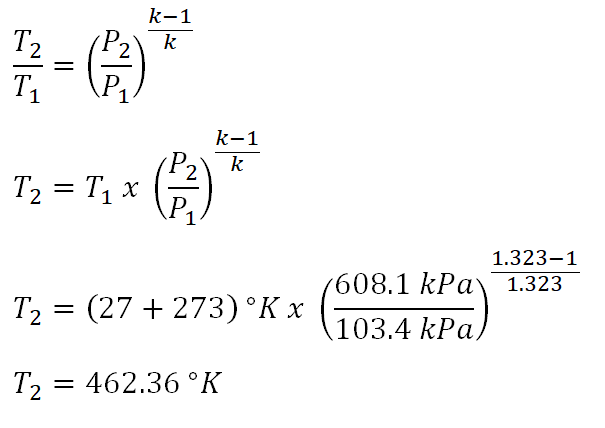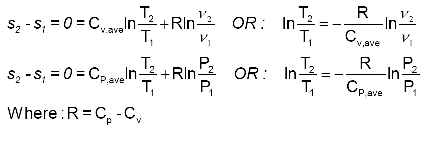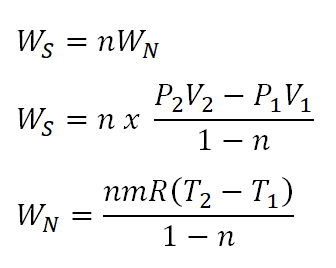Isentropic Process Formula
Consequently in order to maintain constant entropy within the system energy must be removed from the system as heat during the process.

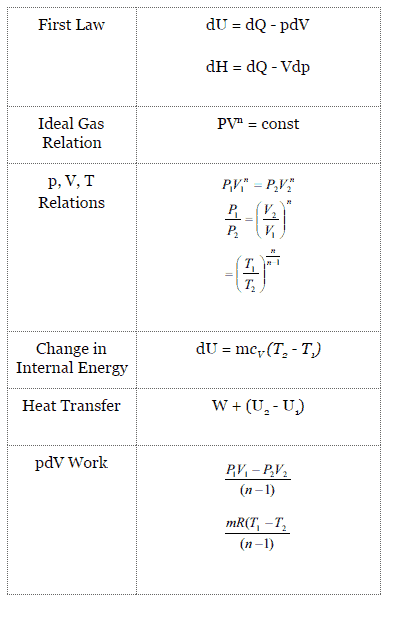
Isentropic process formula. The isentropic process a special case of adiabatic process can be expressed with the ideal gas law as. For a closed system the total change in energy of a system is the sum of the work done and the heat added d u d w d q. The outlet temperature of the gas t 4is can be calculated using p v t relation for isentropic process reversible adiabatic process. The relations of entropy change for ideal gases are 1 and 2 by setting d s to 0 in the above equations the relations for an ideal.
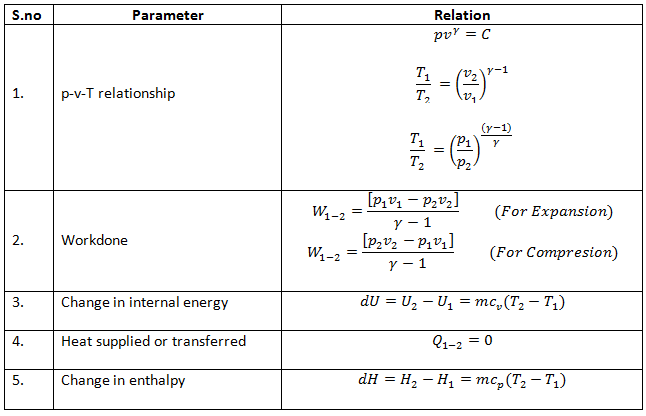
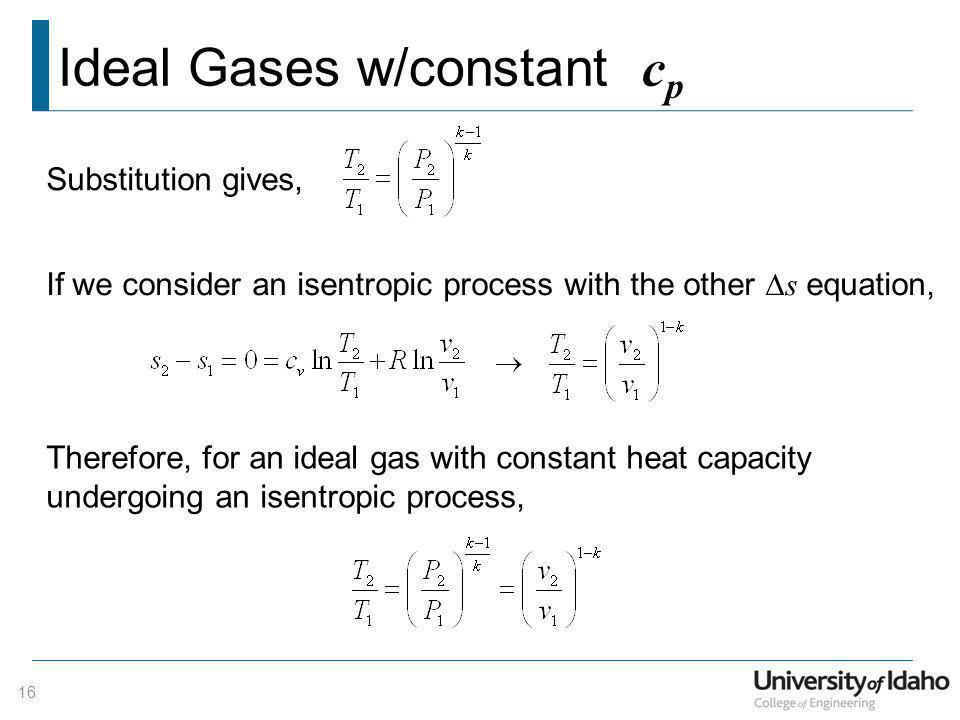
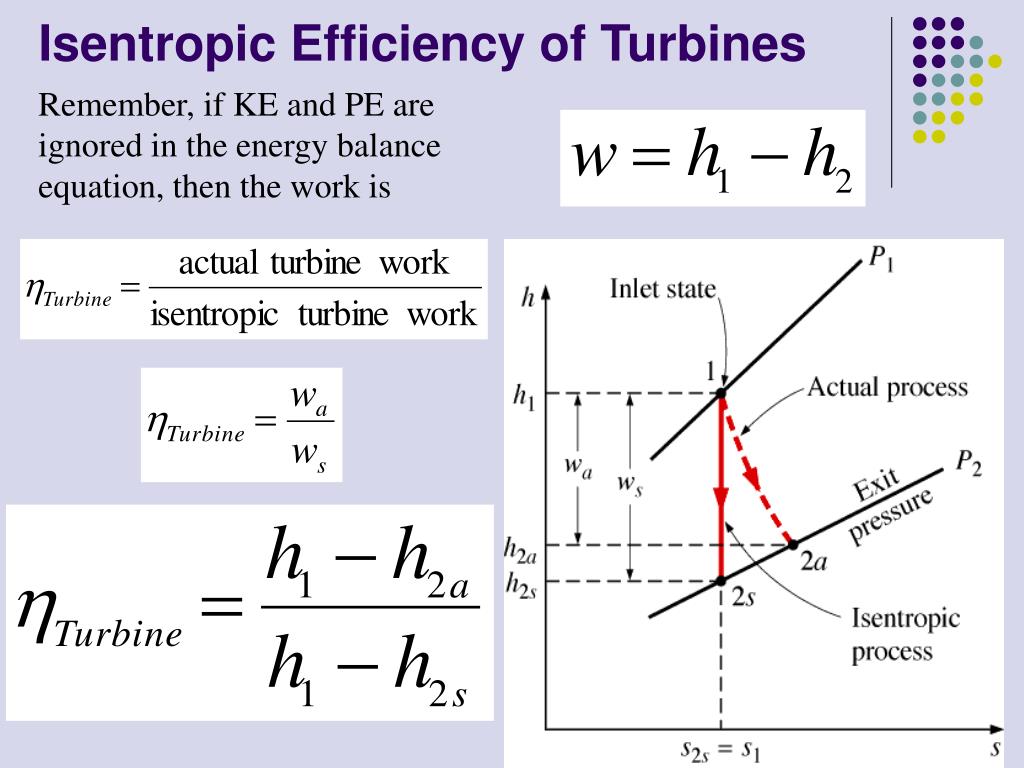
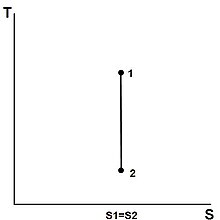
For an ideal gas undergoing isentropic process or. Isentropic processes for ideal gases an isentropic process of ideal gases on a t s diagram. One for constant pressure c p and one for constant volume c v. The work required for the compressor is given by wc h2 h1.
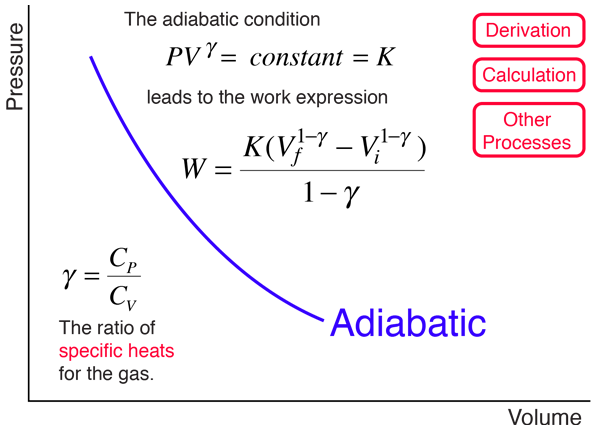
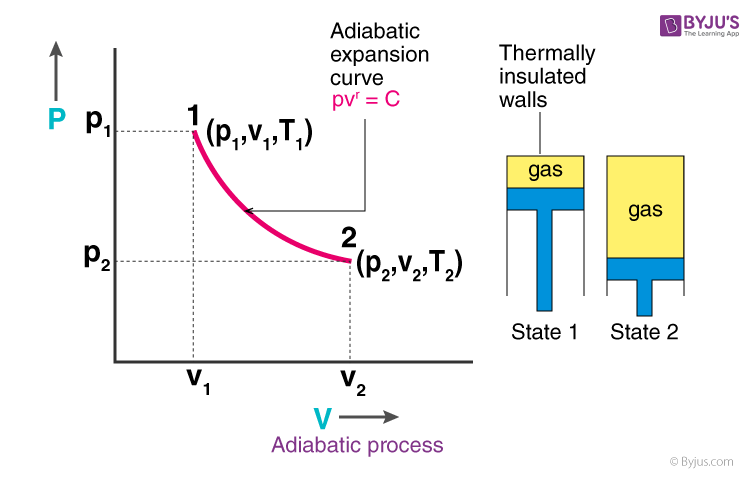
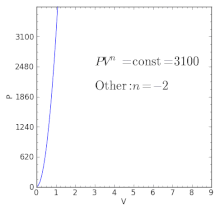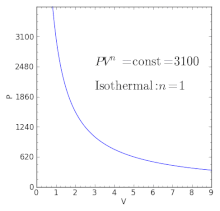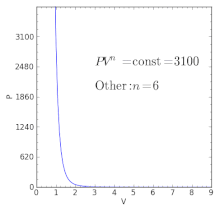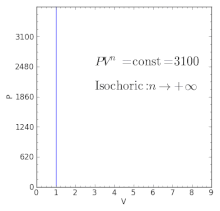
Pv k constant. Isentropic compression ambient air is drawn into the compressor where it is pressurized 1 2. The isentropic process a special case of adiabatic process can be expressed with the ideal gas law as. It is a special case of the adiabatic processes defined as a reversible adiabatic process.
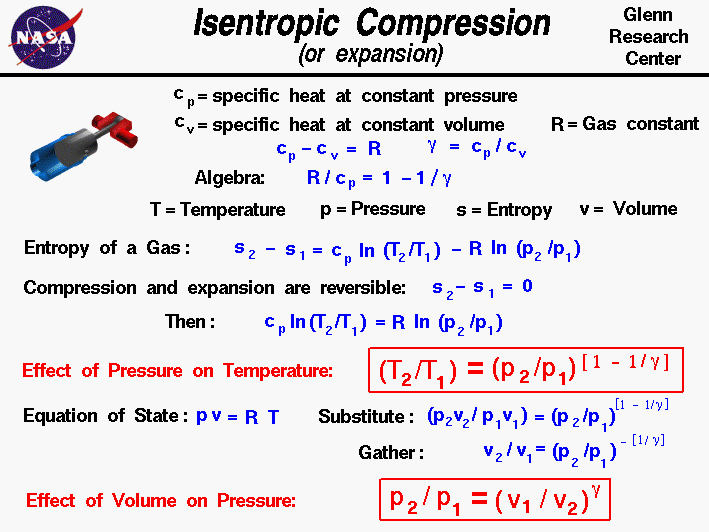
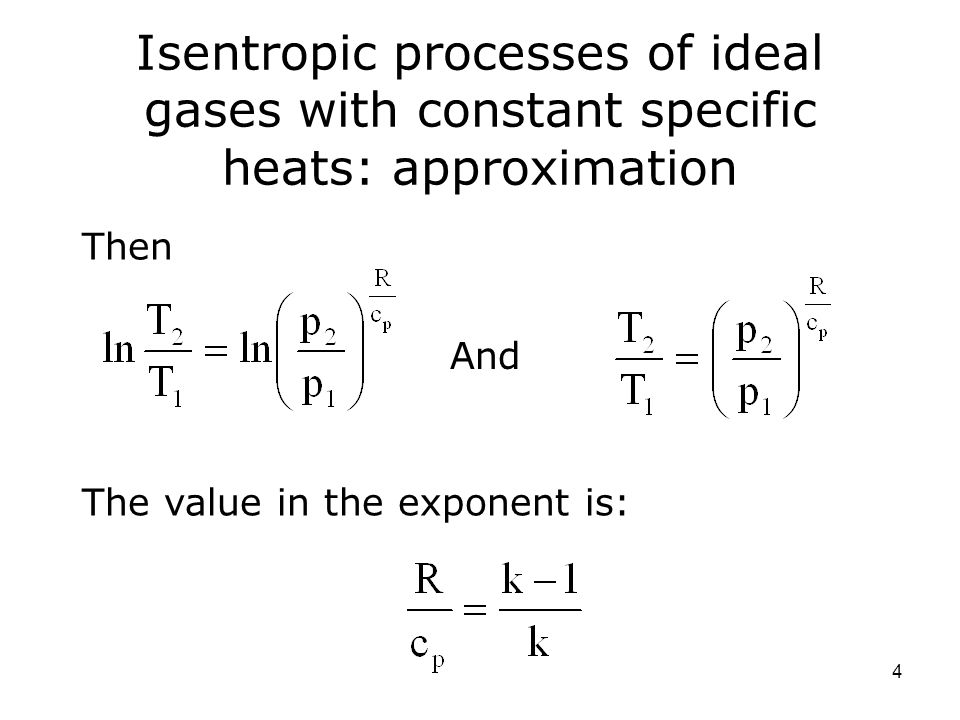
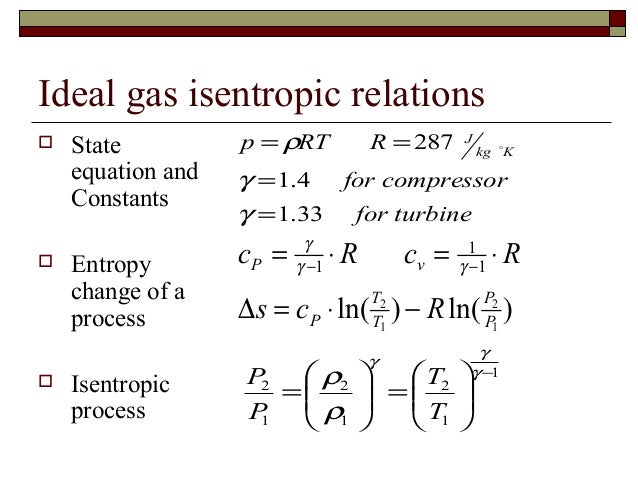
S2 s1 cp ln t2 t1 r ln p2 p1 where the numbers 1 and 2 denote the states at the beginning and end of the compression process s is the entropy t is the temperature p is the pressure and ln denotes the natural logarithm function. Thermodynamic work done on a system undergoing isentropic process is given by. The starred conditions occur when the flow is choked and the mach number is equal to one. In an irreversible process of transfer of energy as work entropy is produced within the system.
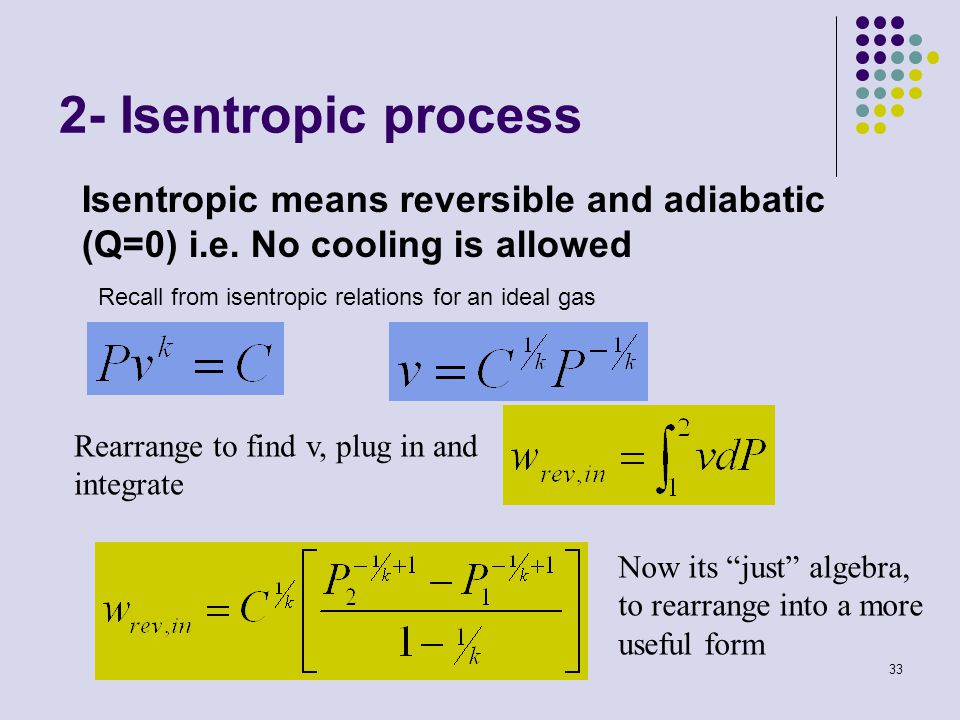
P 1 v 1 k p 2 v 2 k. In which k c p c v is the ratio of the specific heats or heat capacities for the gas. Now we use the equation we have derived for the entropy of a gas. One for constant pressure c p and one for constant volume c v.
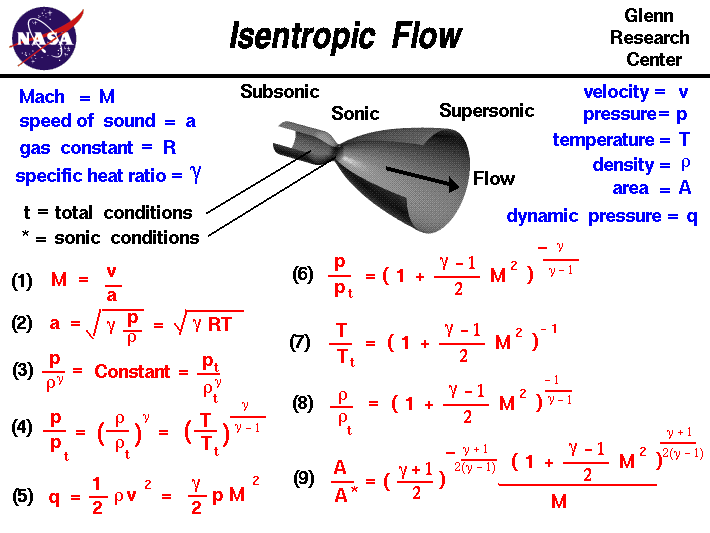
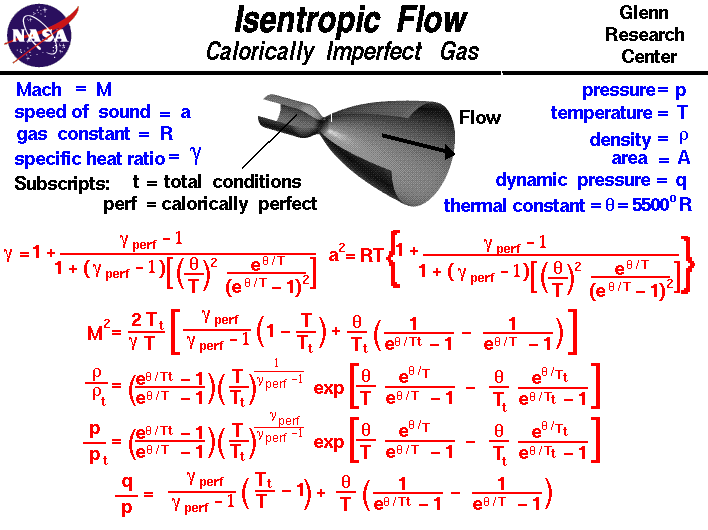
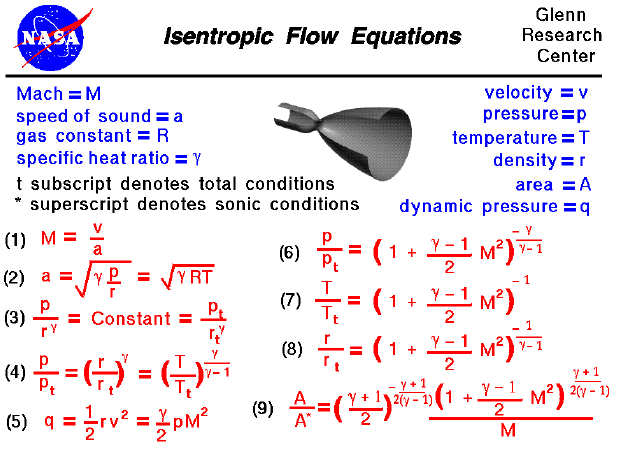
A a 1 m2 gam 12 gam1 gam 12 gam12 gam1 gam 12 m. Isobaric heat addition the compressed air then runs through a combustion chamber where fuel is burned and air or another medium is heated 2 3. P 1 v 1 k p 2 v 2 k. For an isentropic process which by definition is reversible there is no transfer of energy as heat because the process is adiabatic dq 0.
In which k c p c v is the ratio of the specific heats or heat capacities for the gas. Pv k constant. Displaystyle dudelta wdelta q. Notice the important role that the mach number plays in all the equations on the right side of this slide.
Isentropic process is characterized by constant entropy of the system. An isentropic process is an idealization of an actual process and serves as a limiting case for an actual process.